User Datagram Protocol(UDP) by R4R Team
User Datagram Protocol :
UDP stand for (User Datagram Protocol) is a
simple OSI transport layer protocol for client/server network applications based
on Internet Protocol (IP). UDP is the main alternative to TCP and one of the
oldest network protocols in existence, introduced in 1980.
UDP is often used in videoconferencing applications or computer games
specially tuned for real-time performance. To achieve higher performance, the
protocol allows individual packets to be dropped (with no retries) and UDP
packets to be received in a different order than they were sent as dictated by
the application.
UDP datagram header:
A UDP datagram header consists has four fields of two bytes each are given below:
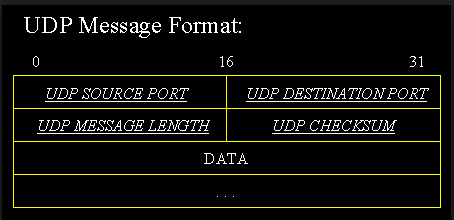
a)udp source port number
b)udp destination port number
c)udp datagram size
d)udp checksum
Features of user datagram protocol(UDP):
Simple protocol
The User Datagram Protocol (UDP protocol) is a very basic and simple protocol on top of the IP protocol
Robustness:
A prominent feature of UDP is its robustness of data delivery over the Internet.
This is the very reason why TCP/IP has mainly standardized UDP for real-time
data transfer, specifically when it comes to the transfer or reception of
voice/video packets over networks. Furthermore, due to this robustness feature,
UDP is also used in services and protocols like domain name system (DNS) and
dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP).
Unreliability:
UDP is fast, but unreliable in nature. This means when data bits are transferred
via UDP, their reception acknowledgment cannot be attained in an automated
fashion, unlike TCP. This feature of UDP prevents it from being used for text or
character transmission/reception on computer networks.
Disarrangement:
Data packets, when sent over a protocol like TCP, arrive in an arranged and
assembled manner at the receiver's end. This property is also missing in UDP,
since it takes no guarantee of transferring data bits or packets in an arranged
manner. This can be stated as the very reason behind its robustness, and
unreliable transmission/reception.
Connectionless:
UDP is not connection oriented.
UDP also have some feature as...
UDP is used when acknowledgement of data does not hold any significance.
UDP is good protocol for data flowing in one direction.
UDP is simple and suitable for query based communications.
UDP does not provide congestion control mechanism.
UDP does not guarantee ordered delivery of data.
UDP is stateless.
Difference between UDP and TCP : are
given below........
| TCP | UDP |
| Reliability: TCP is connection-oriented protocol. When a file or message send it will get delivered unless connections fails. If connection lost, the server will request the lost part. There is no corruption while transferring a message. | Reliability: UDP is connectionless protocol. When you a send a data or message, you don't know if it'll get there, it could get lost on the way. There may be corruption while transferring a message. |
| Ordered: If you send two messages along a connection, one after the other, you know the first message will get there first. You don't have to worry about data arriving in the wrong order | Ordered: If you send two messages out, you don't know what order they'll arrive in i.e. no ordered |
| Heavyweight: - when the low level parts of the TCP "stream" arrive in the wrong order, resend requests have to be sent, and all the out of sequence parts have to be put back together, so requires a bit of work to piece together. | Lightweight: No ordering of messages, no tracking connections, etc. It's just fire and forget! This means it's a lot quicker, and the network card / OS have to do very little work to translate the data back from the packets. |
| Streaming: Data is read as a "stream," with nothing distinguishing where one packet ends and another begins. There may be multiple packets per read call. | Datagrams: Packets are sent individually and are guaranteed to be whole if they arrive. One packet per one read call. |
| Error Checking: TCP does error checking | Error Checking:UDP doesnot error checking, but no recovery options. |
| Connection:TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. | Connectionless:UDP is a connectionless protocol. |
| Function: As a message makes its way across the internet from one computer to another. This is connection based. | Function:UDP is also a protocol used in message transport or transfer. This is not connection based which means that one program can send a load of packets to another and that would be the end of the relationship. |
| Usage: TCP is suited for applications that require high reliability, and transmission time is relatively less critical. | Usage:UDP is suitable for applications that need fast, efficient transmission, such as games. UDP's stateless nature is also useful for servers that answer small queries from huge numbers of clients. |
| Use by other protocols HTTP, HTTPs, FTP, SMTP, Telnet | Used by:DNS, DHCP, TFTP, SNMP, RIP, VOIP. |
| Speed of transfer:The speed for TCP is slower than UDP. | Speed of transfer:UDP is faster because there is no error-checking for packets |
| Header Size: TCP header size is 20 bytes | Header Size :UDP Header size is 8 bytes |
| Common Header Fields:Source port, Destination port, Check Sum | Common Header Fields:Source port, Destination port, Check Sum |
| Examples: World Wide Web (Apache TCP port 80), e-mail (SMTP TCP port 25 Postfix MTA), File Transfer Protocol (FTP port 21) and Secure Shell (OpenSSH port 22) etc. | Examples: Domain Name System (DNS UDP port 53), streaming media applications such as IPTV or movies, Voice over IP (VoIP), Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) and online multiplayer games etc |
| Acknowledgement: Acknowledgement segments | Acknowledgment :No Acknowledgment |
| Checksum: checksum to detect errors | checkmsum: to detect errors |
Leave a Comment:
Search
Categories
- Wireless Application Environment or WAE
- WAP and WAP Gateway Technology.
- Wireless Messaging API (WMA)
- Wireless Markup Language(wml)
- WCDMA technology
- Wireless Datagram Protocol
- User Datagram Protocol(UDP)
- Bluetooth technology (BT)
- iDEN Technology
- Wireless Markup Language Script(WMLScript)
- Wireless Application Environment or WAE
- WAP and WAP Gateway Technology.
- Wireless Messaging API (WMA)
- Wireless Markup Language(wml)
- WCDMA technology
- Wireless Datagram Protocol
- User Datagram Protocol(UDP)
- Bluetooth technology (BT)
- iDEN Technology
- Wireless Markup Language Script(WMLScript)
- J2ME introduction
- Comparison of new mobile technology
- IEEE 802.11 Standards
- API for J2ME
- Basics Components of CLDC
- Standardization through CLDC & MIDP
- Communication and wireless telephony technologies (TDMA, GSM, and CDMA)
- j2me project in diffrent IDE
- Remote method invocation(RMI)
- j2me program example in netbeans IDE
- J2ME Mobile Media API
- Generic Connection Framework (GCF)
- Virtual Machines and its architecture
- Wireless Application Environment or WAE
- Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model
- Deprecated API of J2ME
- Core Java
- Core Java Interview Question Answers
- Hibernate
- Hibernate Interview Question Answers
- Servlet
- Servlet Interview Question Answers
- MYSQL
- MYSQL Interview Question Answers
- JavaServer Pages (JSP)
- JavaServer Pages (JSP) Interview Question Answers
- Spring
- Spring Interview Question Answers
- Struts 2
- Struts 2 Interview Question Answers
- J2ME
- J2ME Interview Question Answers
- General Knowledge
- General Knowledge Interview Question Answers
- Spring boot
- Spring boot Interview Question Answers
- Python
- Python Interview Question Answers
- c language
- c language Interview Question Answers
- C++ language
- C++ language Interview Question Answers
- Data Structure using c
- Data Structure using c Interview Question Answers